ARC, Sydney
ARC, Sydney by Koichi Takada Architects for Crown Group Arc is made up of two 26-storey, 80-meter high towers. The mixed-useA well-integrated mix of different
Tall buildingA tall building is defined as one that is six storeys or more. More forms should be elegant and create positive features in the skyline. Their form, scale and massing must be carefully considered through detailed appraisal and testing including their visual impact on the setting, both individually and when part of a cluster.
Tall buildings must also consider their impact on the street environment and public spaces. Buildings that are too tall can visually overwhelm and cause unwanted side-effects, such as wind funnelling, overshadowing or trapping air pollution.
When tall buildings are viewed from a distance, their building form should be distinctive and identifiable whilst maintaining a positive relationship with their surrounding context.
It is more successful to express the verticality of tall buildings using vertically proportioned grids or patterns. The shape and proportion of window openings should also correspond to the verticality of the building.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:
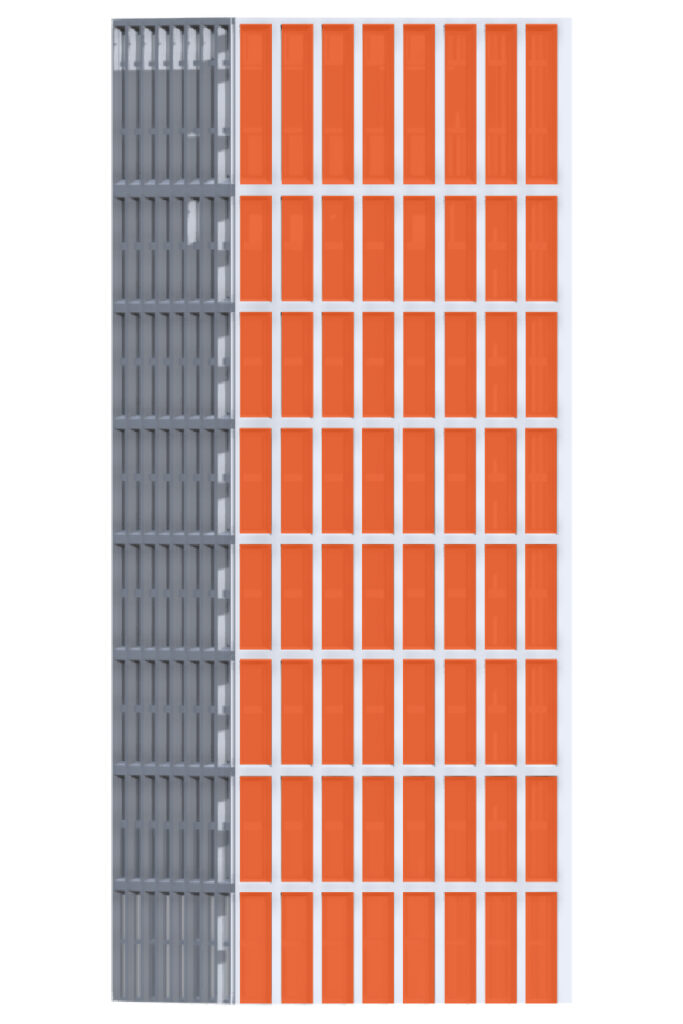
Vertical window openings
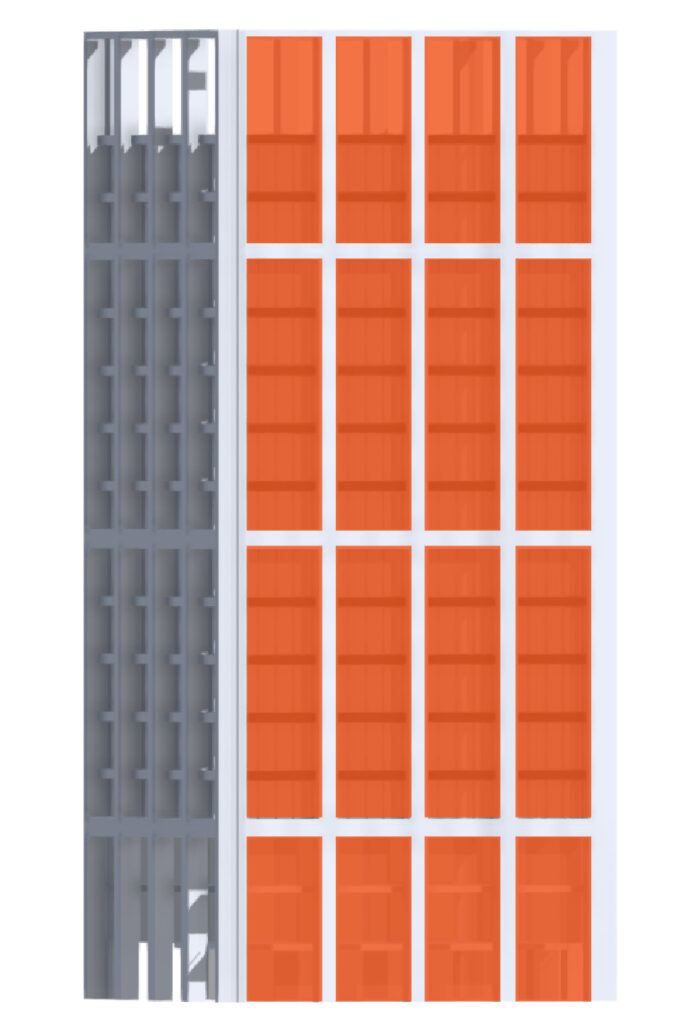
Vertical frame and columns

Vertical and horizontal proportions
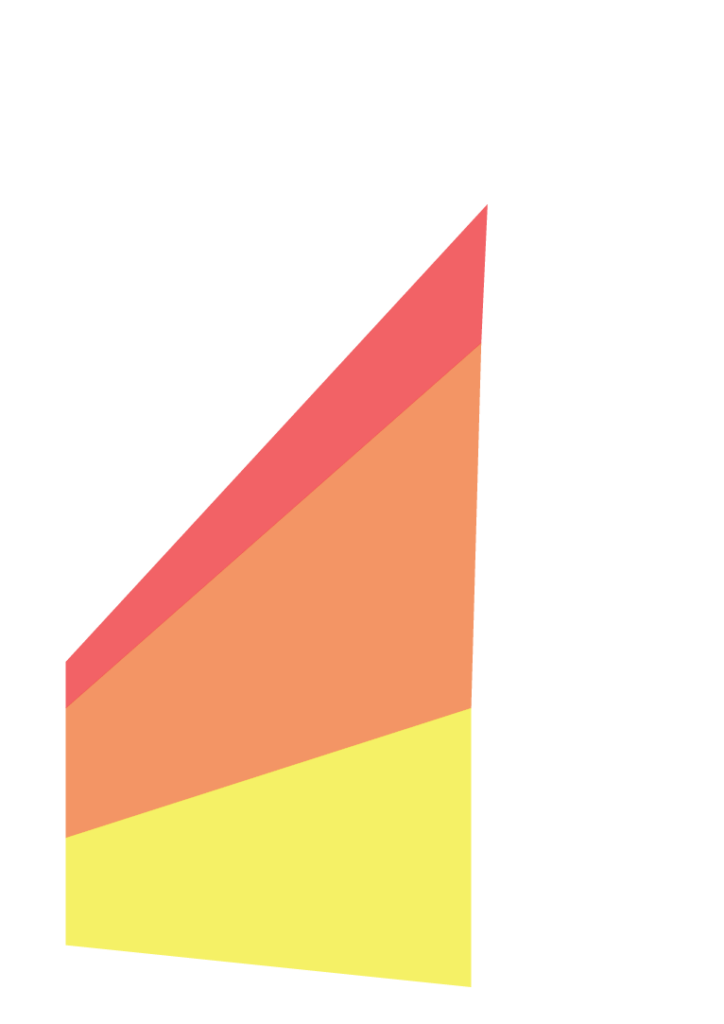
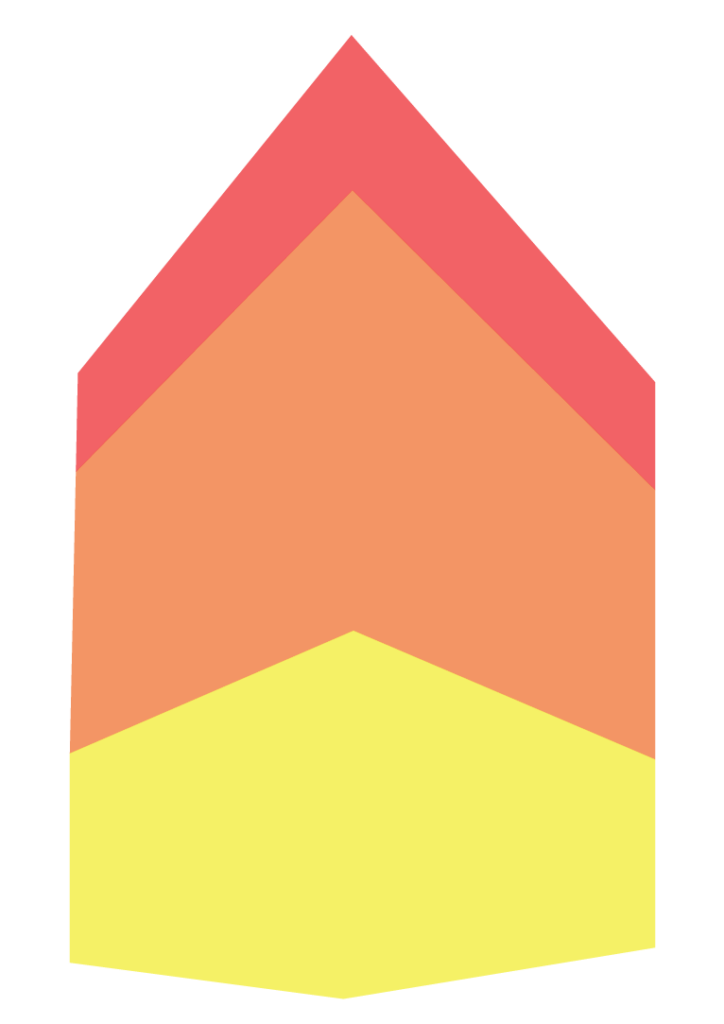
How a tall buildingA tall building is defined as one that is six storeys or more. More meets the ground and sky is critical to its success. The standard architectural convention of a base, middle, top.
Tall buildings should be grounded, creating a sense of permanence and presence. This should be articulated through a regular, repeating bay rhythm or through a more solid elevation with emphasised openings. Double or triple height ground floor spaces should be created with active uses planned at strategic places to deliver a human scaleThe use within development of elements which relate well in size to an individual human being and their assembly in a way which makes people feel comfortable rather than overwhelmed. More and enliven the street at different times of the day. The quality of material, detailingThe details of a building are the individual components and how they are put together. Some are a deliberate part of the appearance of a building, including doors, windows and their surrounds, porches, decorative features and ironmongery. Others are functional, although they can also contribute to the appearance of a building. These include lighting, flues and ventilation, gutters, pipes and other rainwater details. Detailing affects the appearance of a building or space and how it is experienced. It also affects how well it weathers and lasts over time. More, glazing and fenestration should articulate the street level interface as a distinct section of the building. This should integrate into the rest of the built environment. Particular consideration should be given to the materials and detail used at ground floor level where materials should enhance the street level experience and respond to the local context.
The middle section can make use of an elevational grid to respond to either residential or commercial uses which can be expressed as simple repetition or expressed bays.
Options to terminate the building to the skypoint (top) include elevation rhythm change, crown, hipped corners and decorative caps. Any rooftop plant should be integrated into the architecture to create a well-conceived silhouette.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:

A variety of land uses can be used to activate ground floor and they should be mixed to ensure people activity throughout the day.
Offices and retail leisure units on bottom three floors. The first floor can overhang to create a covered collonade for certain uses.

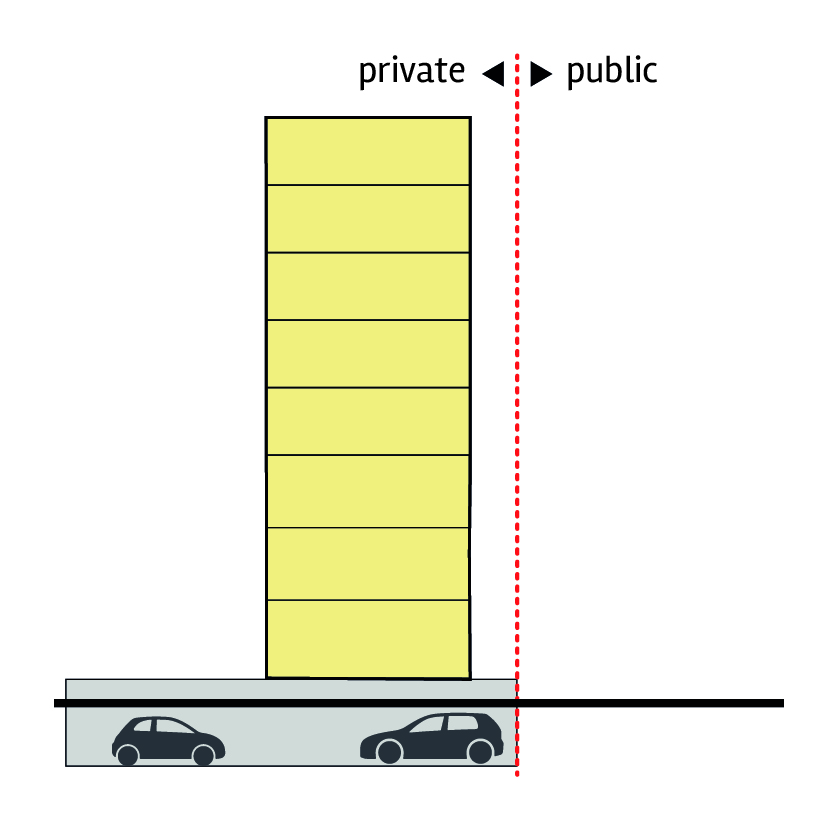
Retail, cafes, restaurants or other leisure uses on bottom two floors of building with parking podium to rear
Key

Offices on two ground floor levels with basement parking to allow access to rear communal area
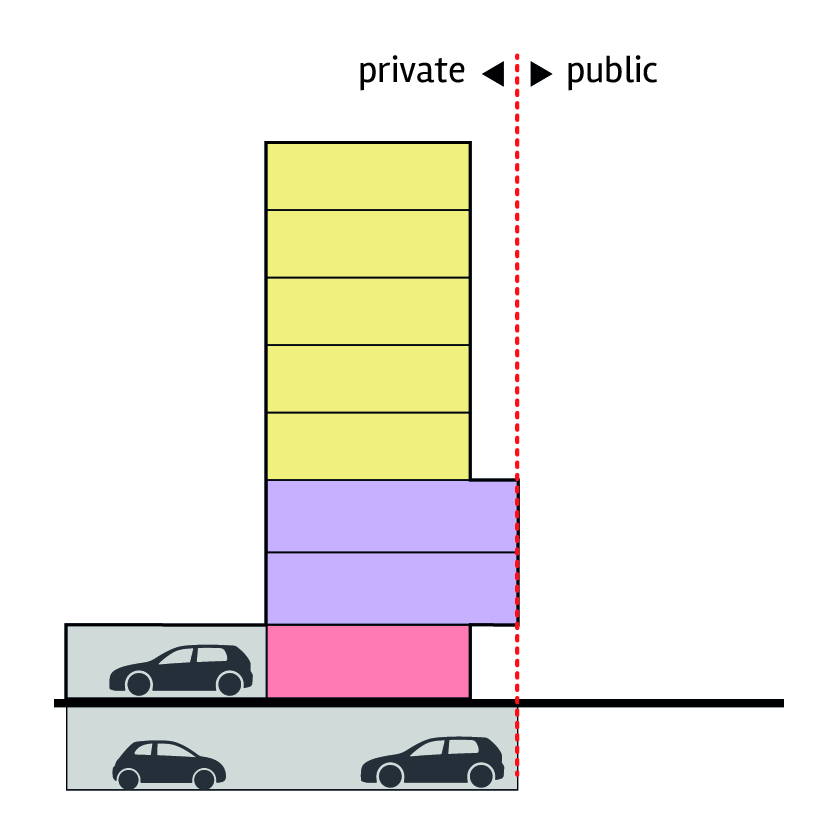
Residential uses are possible on ground floor but should be set back to allow for private entrances and a space between public boundary
People like sunlight, it is seen as providing light and warmth, making spaces and rooms look bright and cheerful and also having a therapeutic health-giving effect.
Solar studies should be used to demonstrate that new development is in general compliance with the guidelines set out in the Building Research Establishment guidance in terms of the impacts of daylight, sunlight and overshadowing, including the two-hour sun on ground analysis.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:
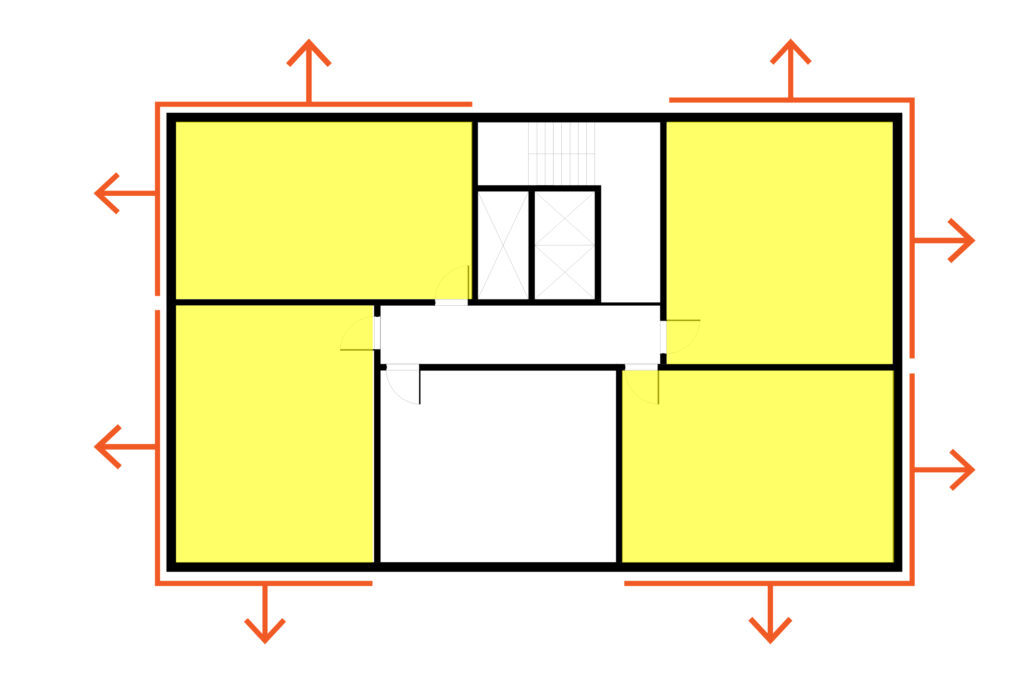
Internal corridor slab; Apartment units in a long horizontal shape building should have longest elevations facing south and place core or services on north elevation

Internal corridor tower; apartments with small floorspace can maximize dual aspectDual aspect houses or apartments have been designed to have [openable] windows on two or more walls, allowing for increased levels of natural daylight, sunlight and cross ventilation. More apartments and have core on northern elevation
The development of tall buildings can lead to wind microclimate impacts. These issues can impact on the safety and comfort of pedestrians as a result of wind speeds and wind tunnelling. Developments must be designed and assessed to ensure that no detrimental wind microclimate impacts arise as a result of developments.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:
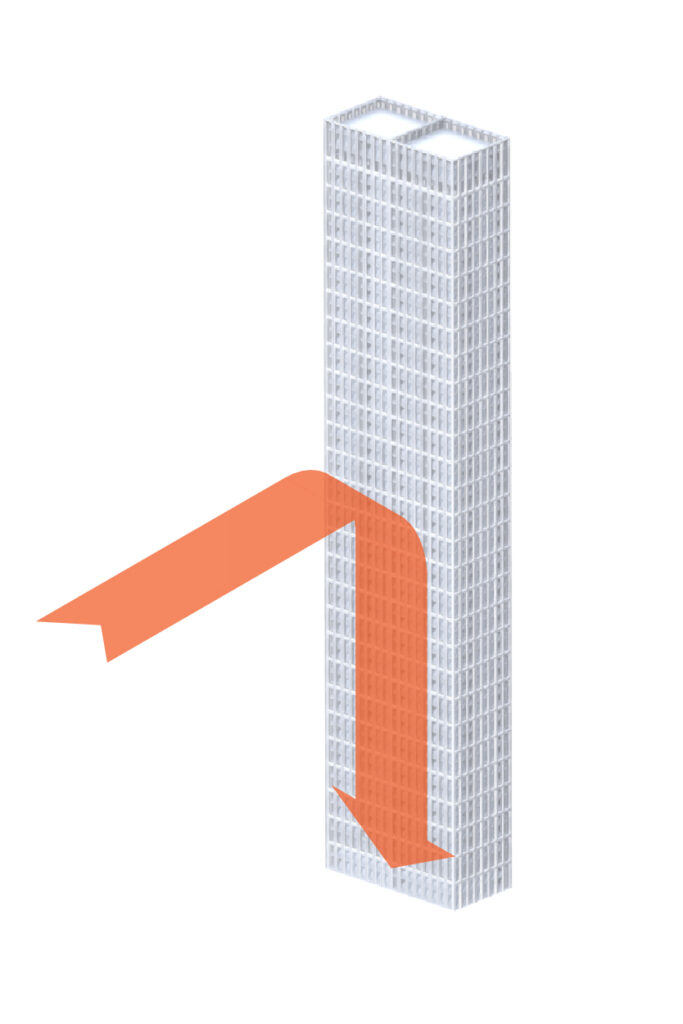
Consider how the impact of downdraught can be mitigated to reduce negative impact of high speeds at street level

Consider impact of moving wind around a curved building and how that can impact surrounding context

ARC, Sydney by Koichi Takada Architects for Crown Group Arc is made up of two 26-storey, 80-meter high towers. The mixed-useA well-integrated mix of different

Egham Gateway master plan by Allford Monaham Morris Egham Gateway is a new mixed use developmentA well-integrated mix of different land uses which may include retail, employment, leisure and other service uses with decent homes of different types and tenures to support a range of household sizes, ages and incomes. More in the Runnymede borough of Surrey. Four mixed useA well-integrated mix of different land uses which may include retail, employment, leisure and other service uses with decent homes of different types and tenures to support a range of household sizes, ages and incomes. More

Botanica Apartments by Tim Groom Architects The site occupies a highly prominent location alongside the Bridgewater Way, a major arterial road running south west from







