Streets and Public Realm
Street Types
Introduction
A contextualThe context includes the immediate surroundings of the site, the neighbourhood in which it sits and the wider setting. The context may include the physical surroundings of topography, movement patterns and infrastructure, built form and uses. An understanding of the context, history and character of an area must influence the siting and design of new development. More response will result in the definition of any number of street types. The guidance here describes five defined street types, ranging from highest to lowest place value.
The applicant is expected to identify their street hierarchyCategorises street and roads according to their functions and capacities. More and fully justify the definition of streets within their plan. The following graphics outline the balance of place and movement when considering the defined street hierarchyCategorises street and roads according to their functions and capacities. More in Trafford.
Diagram key for all street types
Slow active travel (walking, wheelchairs, pushchairs)
Fast active travel (cycles, mobility scooter, scooters)
Furnishing zones (furniture, lighting, dining areas)
Road infrastructure (carriageway, bus stops)
Parking (cars, deliveries, electrical charging)
Green / blue infrastructure (SUDsSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More, street trees)
Pedestrian footway
Wheelchair accessible
Cycle accessible lane
Scooter accessible lane
Mobility scooter accessible lane
Buffer zone for cycle lanes
Furnishing zone
Outdoor dining zone
Carriageway for cars
On-street parking and charging
Street trees
Sustainable Urban DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More
Destination Streets
These places are critical to the success of our towns and urban environments. They often form the heart of our communities and therefore re enforce social cohesion, civic pride and foster a sense of community. Due to the important role these places play, their performance is intrinsically linked to the success of our communities.
Destination places are those primarily designed for and used by people, where there are few, or no, vehicles. These places provide space for people to meet and socialise. They may provide opportunities for play and space to host events. Green infrastructure will enhance these places by; providing shade and reducing the heat island effect in summer, being part of a sustainable drainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More system helping to mitigate the effects of stormwater runoff, contributing to increased biodiversity and making the place attractive.
Characteristics
• High quality materials
• Street trees
• Sustainable DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More Systems
• Places to sit
• Pedestrian dominated with dedicated space along building line
• Cycle parking
• If vehicles do require access then this must be time limited and low speed

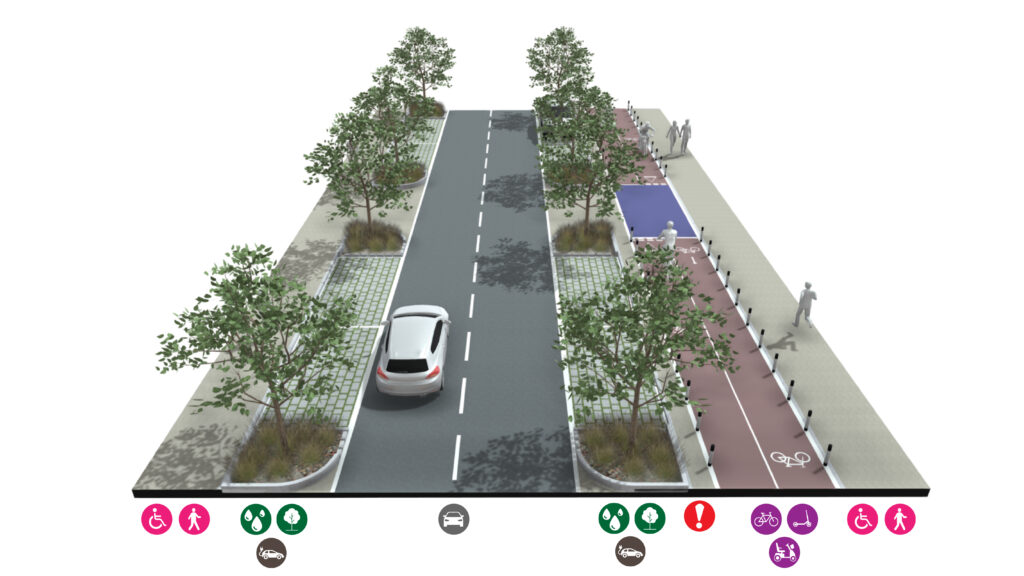
Local Streets
Local streets are where people live, they are both movement corridors and places where people meet providing physical connections to the wider community and a social connection with neighbours. Cycling should also be an easy and safe way to get around using these streets and they should be designed for low vehicle speeds.
Characteristics
• Wide footways
• Potential for cycle streets
• Street trees
• Sustainable DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More Systems
• Slow vehicle environment (20mph limit)
• On-street parking
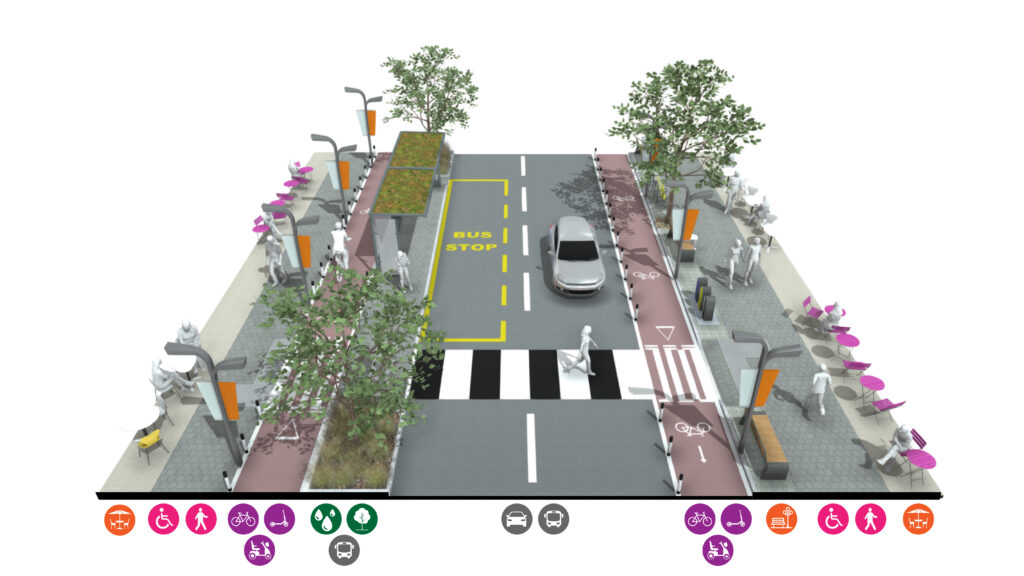
High Streets
The social and economic prosperity of our towns and villages is intrinsically linked to our high streets. Designed and delivered successfully, high streets will benefit immediate and neighbouring communities.
High Streets form the social and economic heart of our towns and villages.
They provide local employment and amenities for residents. Shops, cafes, bars and restaurants provide activity and vitality to our neighbourhoods, activating our streets. By their mixed useA well-integrated mix of different land uses which may include retail, employment, leisure and other service uses with decent homes of different types and tenures to support a range of household sizes, ages and incomes. More nature, high streets have high volumes of movement from all transport forms. To be successful, high streets must balance the priorities of these users.
Characteristics
• Wide footways
• Street trees
• Cycle lanes, cycle parking
• Sustainable DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More Systems
• Slow vehicle environment
• Bus lane if space allows
• Variety of crossing points
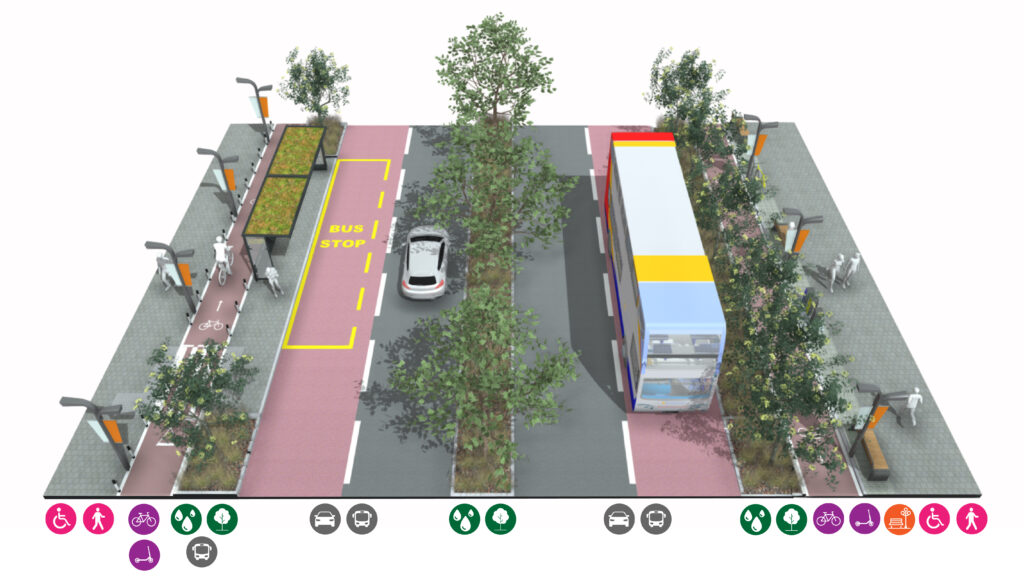
Connector Roads
Connector roads provide an important role in linking neighbourhoods and communities. These are focused more on the priorities of vehicles rather than the needs of people. They should contain some features that make them good places to be (inc. shops, bus stops, green space and street furnitureThe collective name used for all furniture, fittings and objects in the external areas of buildings, landscapes and streets for the benefit of the public. This can include benches, post boxes, cycle stands, traffic lights, street lamps, traffic signs, outdoor sculptures, and waste bins that are seen on the street. More/ lighting), as well as attractive and ecologically diverse corridors. Sustainable and active forms of transport should be prioritised, creating or enhancing bus lanes and cycle routes.
Connector roads should utilise green infrastructure to reduce environmental impacts of road traffic such as noise and air pollution. Trees and planting should be used as a means of capturing and storing surface water from the carriageway, creating a more resilient environment.
Characteristics
• Clear footways
• Cycle lanes
• Bus lanes, if space, or bus priority measures
• Sustainable DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More Systems
• ‘Floating’ parking lane if space allows
• Safe crossing points
• Street trees
• Places to sit
• Formal & informal crossing points, median strip
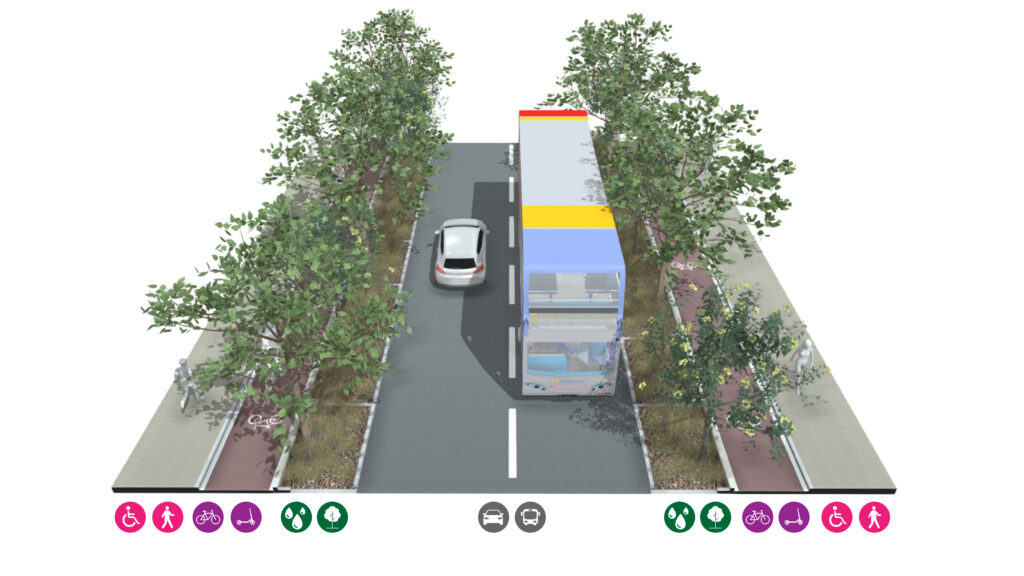
Strategic Roads
Strategic roads carry many vehicles, particularly for longer journeys providing routes to the motorway network and between towns and places. Active modes of transport such as cycling and walking may follow similar routes that are segregated from the road in rural areas.
Strategic roads should utilise larger-scale green infrastructure to reduce the environmental impacts of road traffic such as noise and air pollution. Trees, swales, and woodland should be used as a means of capturing and storing surface water from the carriageway, screening strategic roads, and providing additional habitat area.
Characteristics
• Clear footways
• Cycle lanes (fully segregated out of town,
potentially a shared path with pedestrians)
• Sustainable DrainageSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More Systems
• Signalised crossings at busy locations