Urban Environment House, Helsinki
Urban Environment House, Helsinki by Lahdelma & Mahlamäki Architects The Urban Environment House is a building designed by Lahdelma & Mahlamäki architects for the Urban
As a general rule development should seek to reduce the visual dominance of cars and other vehicles on the public realmThis is the space between and within buildings that is publicly accessible, including streets, squares, forecourts, parks and open spaces. More and design out inconsiderate parking which affects streets in and around developments.
Cycle parking must be located conveniently and planned to ensure easy access, encouraging day-to-day usage. It should feel secure giving cyclists confidence that their bicycle will still be there when they return and with good levels of natural surveillance to help users feel safe.
Surface parking must be well-designed with high quality hard and soft landscaping. Surface parking areas must benefit from natural surveillance and developments designed to prevent indiscriminate car parking such as parking on verges and pavements.
Please read Code LNIP1 Commercial and industrial site layouts.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:
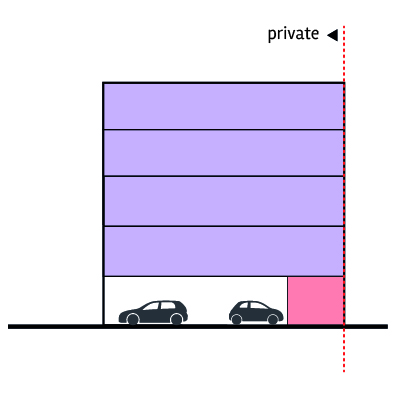
Surface car parking behind building
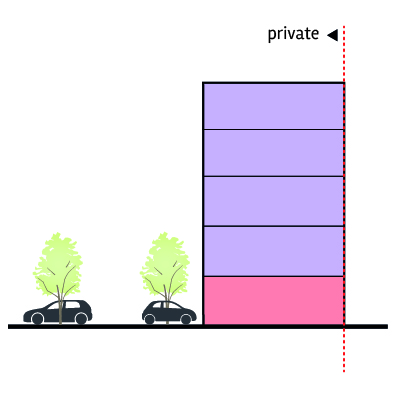
Surface parking with decked communal area

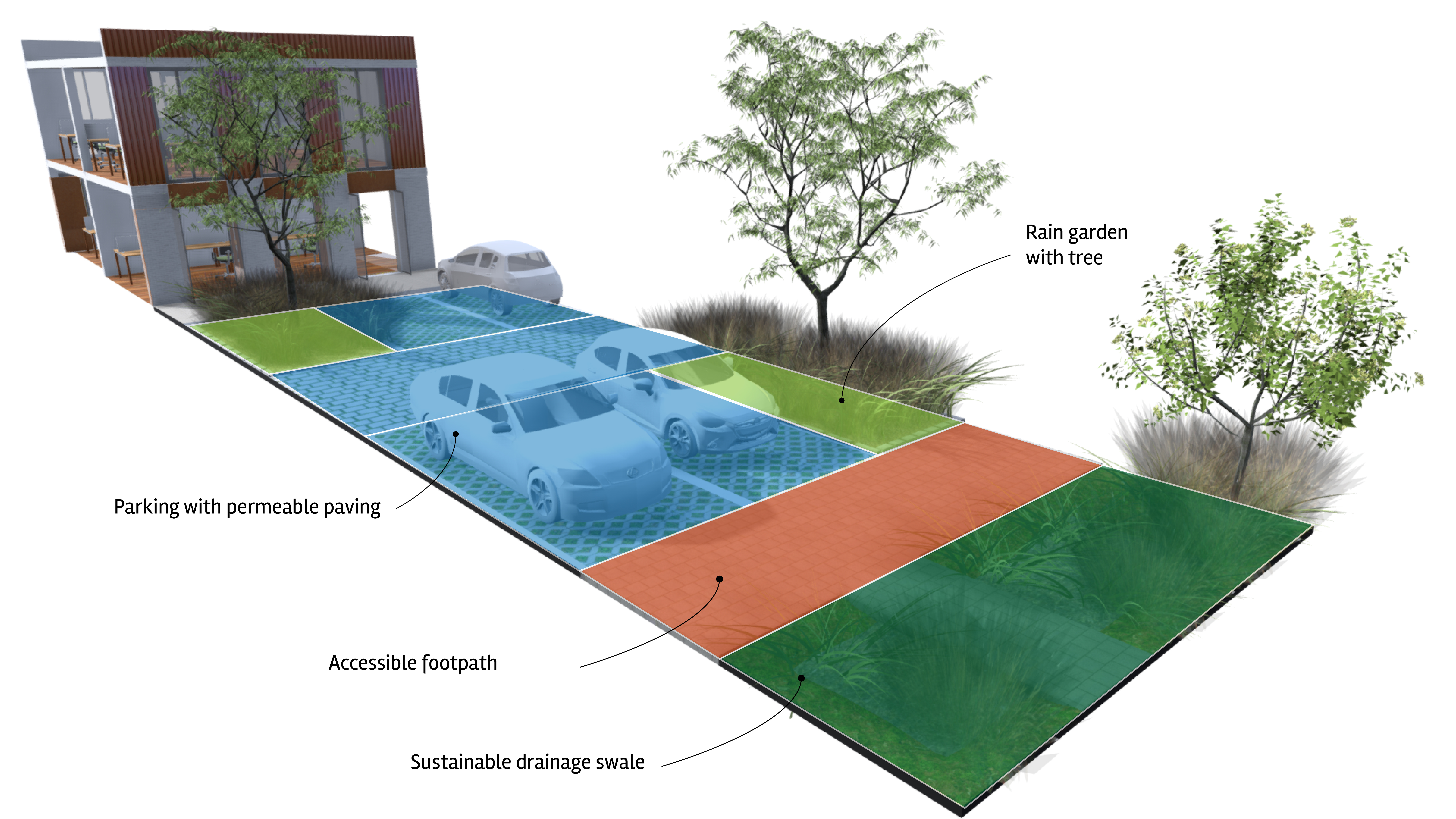
SUDsSuDS are a natural approach to managing drainage in and around properties and other developments. Sustainable drainage measures are ones which avoid adding to flood risks both at a development site and elsewhere in the catchment by replicating natural drainage processes. SuDS work by slowing and holding back the water that runs off from a site, alleviating flooding and allowing natural processes to break down pollutants. More swale
Rain garden
Accessible path
Parking
Undercroft parking (ground level parking under buildings which have open sides) should only be used where it can be adequately concealed from principal elevations by active ground floor uses. Where undercroft parking is considered to be acceptable it must be obscured from view from the street, form an integral part of the overall elevation design, with openings kept to a minimum.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with. Retaining walls should be clearly shown on floorplans, elevations and sections.
Documents required:
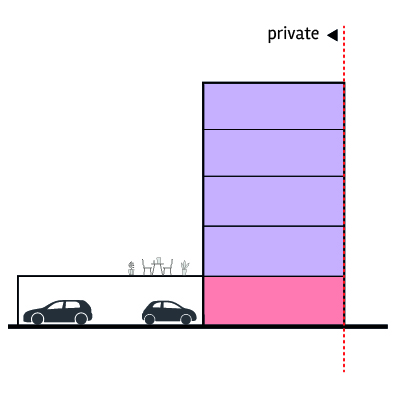
Undercroft parking with retail edge on street
Undercroft and deck parking



Office
Active ground floor
Parking
Well-designed basement parking can negate the clutter associated with surface parking if the vehicular entrance and associated retaining walls are concealed from the public realmThis is the space between and within buildings that is publicly accessible, including streets, squares, forecourts, parks and open spaces. More. The design of basement parking areas must be integral to the overall architecture of the building and the landscaping of the site, with retaining walls kept to a minimum. However, the introduction of basement parking in existing buildings will generally not be supported because of the negative effect it has on the characterCharacter includes all of the elements that go to make a place, how it looks and feels, its geography and landscape, its noises and smells, activity, people and businesses. This character should be understood as a starting point for all development. Character can be understood at three levels; the area type in which the site sits, its surroundings and the features of the site. More of the building.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with. Retaining walls should be clearly shown on floorplans, elevations and sections.
Documents required:


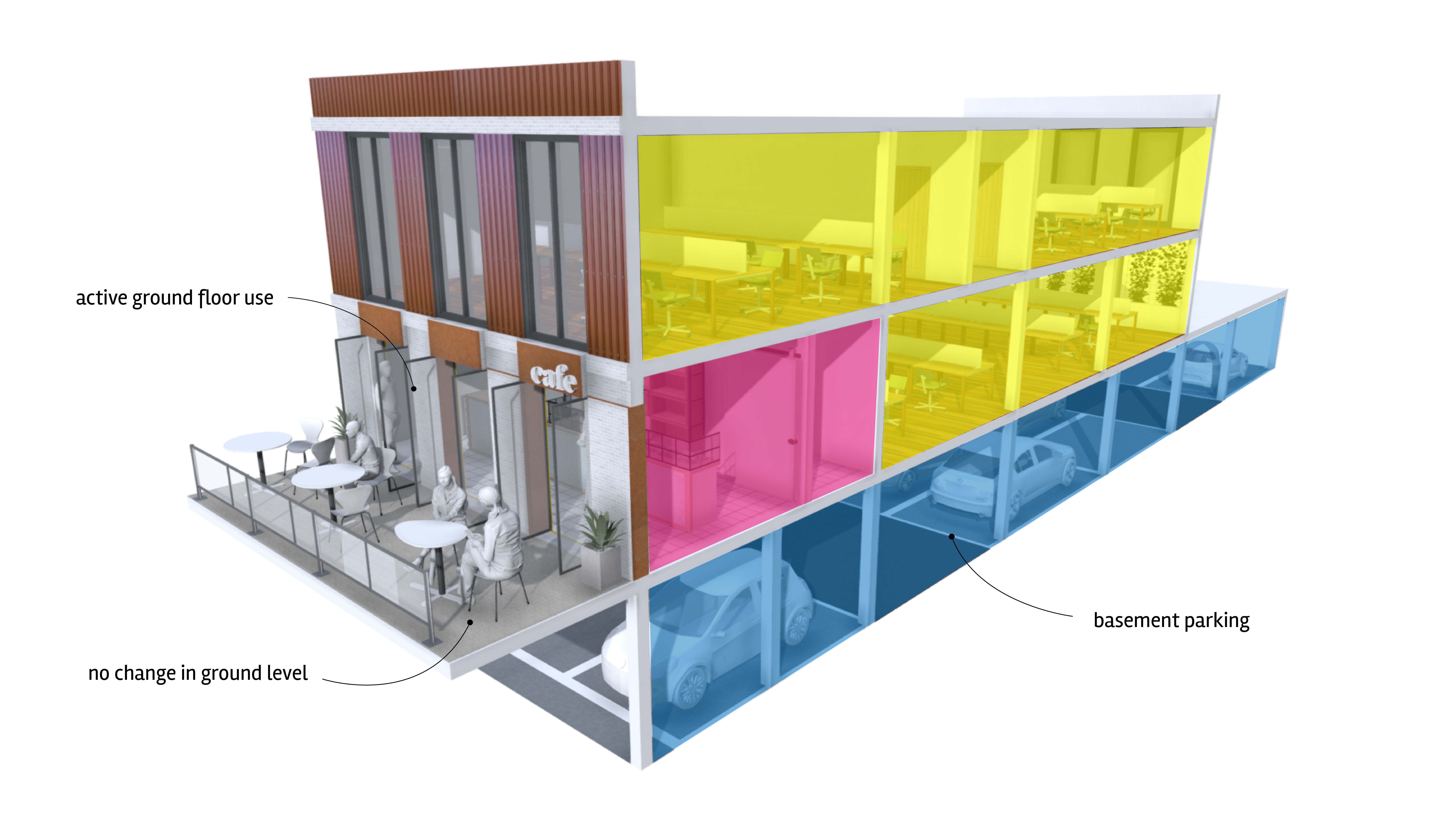
Office
Active ground floor
Parking
Cycle parking must be provided in a covered, secure and easily accessible location and provide for a range of cycle types.
Applicants should refer to the Council’s cycle parking standards to establish the quantum of cycle parking required. Cycle parking for non-residential uses should be integrated into the main building, but where this is not possible cycle storage areas must be covered, secure and within close proximity to the building entrance. External cycle stores must be well-designed and sited where they do not detract from the characterCharacter includes all of the elements that go to make a place, how it looks and feels, its geography and landscape, its noises and smells, activity, people and businesses. This character should be understood as a starting point for all development. Character can be understood at three levels; the area type in which the site sits, its surroundings and the features of the site. More and appearance of the building or the surrounding area. Five percent of all cycle parking spaces should be capable of accommodating inclusive cycles, cargo cycles and tricycles.
Applicants should demonstrate in their submission how this element of the Code has been complied with.
Documents required:

Urban Environment House, Helsinki by Lahdelma & Mahlamäki Architects The Urban Environment House is a building designed by Lahdelma & Mahlamäki architects for the Urban

Wellington Place, Leeds by DLG, Arup, Feilden Clegg Bradley Studios Architects (FCBS), Carey Jones and Gillespies, Martha Schwartz (Landscape) Wellington Place marks an important part
Trafford Council, Trafford Town Hall, Talbot Road, Stretford, M32 0TH







